Locate Events on a Map
Introduction
This tutorial goes through the steps needed to create a Google Map populated with events taking place in a specific area on the map. Given the lat/lon value pair provided by the Google Maps API, a search call is triggered in the Discovery API with that value in a radius of 25 miles, which is the default value if none is set.
Authentication
To run a successful API call, you will need to pass your API Key as the query parameter apikey.
Example: https://app.ticketmaster.com/discovery/v2/events.json?{apikey}
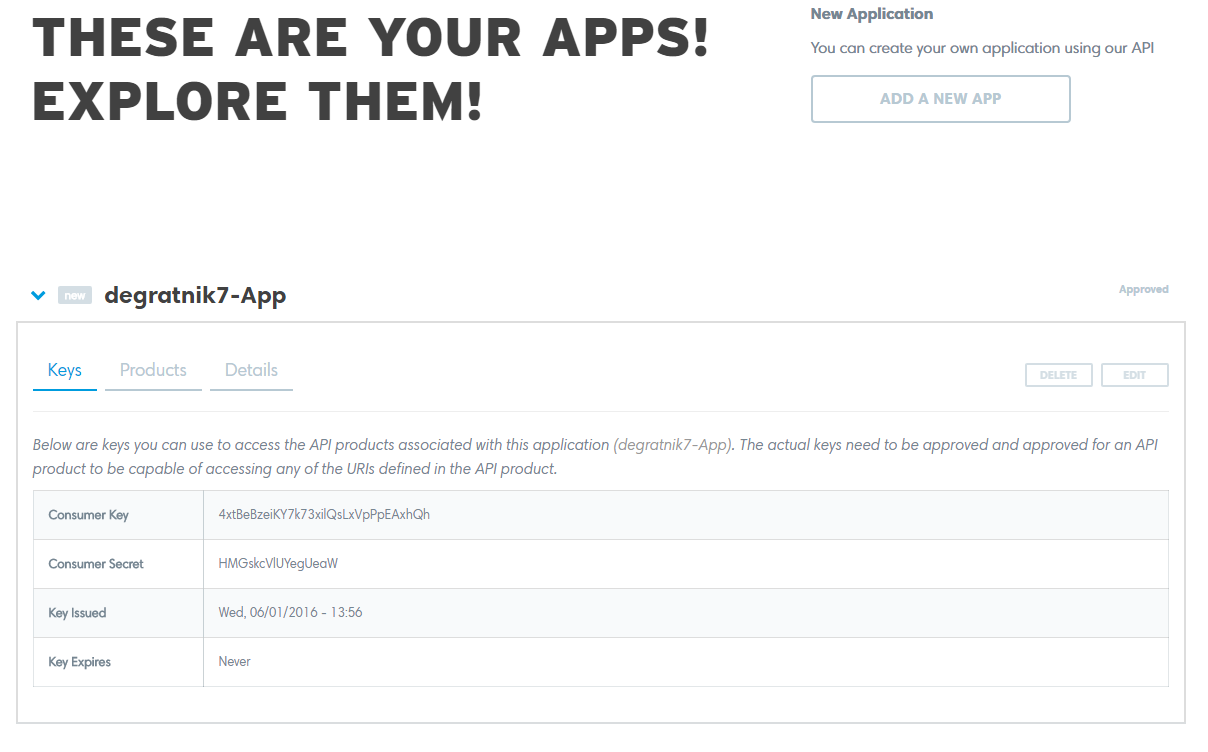
Get an API key
Register on the developers portal. After the registration, the default application will be created. The application contains a Consumer Key that is used for authentication.
Your Consumer Key is your API Key.
Events on a map
Here’s a simple page with a Google map and markers for events:
Events on a map
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.12.2/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p id="location">location there</p>
<div id="map"></div>
<div id="events"></div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
<script src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js" async defer></script>
</body>
</html>function getLocation() {
if (navigator.geolocation) {
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(showPosition, showError);
} else {
var x = document.getElementById("location");
x.innerHTML = "Geolocation is not supported by this browser.";
}
}
function showPosition(position) {
var x = document.getElementById("location");
x.innerHTML = "Latitude: " + position.coords.latitude +
"<br>Longitude: " + position.coords.longitude;
var latlon = position.coords.latitude + "," + position.coords.longitude;
$.ajax({
type:"GET",
url:"https://app.ticketmaster.com/discovery/v2/events.json?apikey=pLOeuGq2JL05uEGrZG7DuGWu6sh2OnMz&latlong="+latlon,
async:true,
dataType: "json",
success: function(json) {
console.log(json);
var e = document.getElementById("events");
e.innerHTML = json.page.totalElements + " events found.";
showEvents(json);
initMap(position, json);
},
error: function(xhr, status, err) {
console.log(err);
}
});
}
function showError(error) {
switch(error.code) {
case error.PERMISSION_DENIED:
x.innerHTML = "User denied the request for Geolocation."
break;
case error.POSITION_UNAVAILABLE:
x.innerHTML = "Location information is unavailable."
break;
case error.TIMEOUT:
x.innerHTML = "The request to get user location timed out."
break;
case error.UNKNOWN_ERROR:
x.innerHTML = "An unknown error occurred."
break;
}
}
function showEvents(json) {
for(var i=0; i<json.page.size; i++) {
$("#events").append("<p>"+json._embedded.events[i].name+"</p>");
}
}
function initMap(position, json) {
var mapDiv = document.getElementById('map');
var map = new google.maps.Map(mapDiv, {
center: {lat: position.coords.latitude, lng: position.coords.longitude},
zoom: 10
});
for(var i=0; i<json.page.size; i++) {
addMarker(map, json._embedded.events[i]);
}
}
function addMarker(map, event) {
var marker = new google.maps.Marker({
position: new google.maps.LatLng(event._embedded.venues[0].location.latitude, event._embedded.venues[0].location.longitude),
map: map
});
marker.setIcon('http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/ms/icons/red-dot.png');
console.log(marker);
}
getLocation();#map {
width: 500px;
height: 400px;
}When rendered, the page will show the map below:
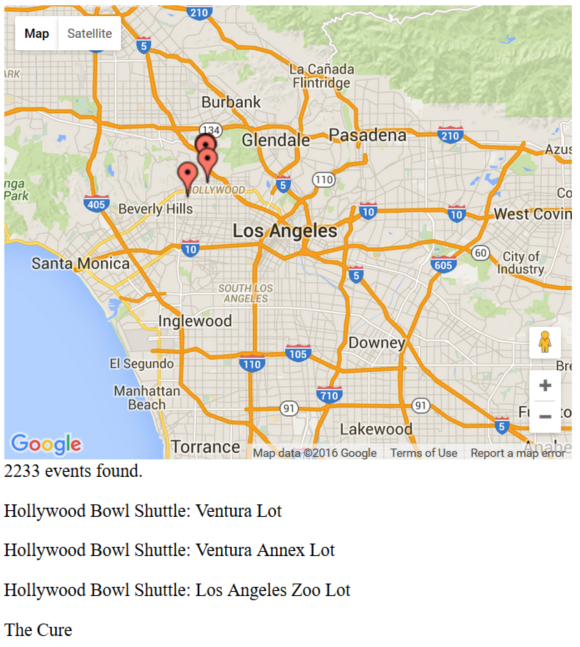
Great! Now let’s dive into the details.
Using the Google Map API
The page has a simple layout. We start by including CSS and jQuery in the head tag. You will see that in all out tutorials.
Inside the body element, there are two div elements. One with id="map" for the rendering of the Google map. The second with id="events" to render the list of events marked on the map.
Below the divs, we include our own script, which we will discuss later, and the Google Maps API <script src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js" async defer></script>.
Using The Google Map API
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.12.2/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p id="location">location there</p>
<div id="map"></div>
<div id="events"></div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
<script src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js" async defer></script>
</body>
</html>Getting the browser’s geolocation
Geolocation is a standard feature in HTML5. All modern browsers support it.
When you try to use geolocation in JavaScript, a browser will ask a user for permission:
Getting The Browser’s Geolocation
function getLocation() {
if (navigator.geolocation) {
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(showPosition, showError);
} else {
var x = document.getElementById("location");
x.innerHTML = "Geolocation is not supported by this browser.";
}
}
function showError(error) {
switch(error.code) {
case error.PERMISSION_DENIED:
x.innerHTML = "User denied the request for Geolocation."
break;
case error.POSITION_UNAVAILABLE:
x.innerHTML = "Location information is unavailable."
break;
case error.TIMEOUT:
x.innerHTML = "The request to get user location timed out."
break;
case error.UNKNOWN_ERROR:
x.innerHTML = "An unknown error occurred."
break;
}
}There are two functions defined above: getLocation and showError.
getLocation tries to get the location navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(showPosition, showError); and in a case of an error, it calls showError, which in turn checks the error code and displays the appropriate message back to the user.
Assuming no errors are encountered, now we have your current location in a lat/lon value pair.
Passing location to the Discovery API
Now we make an API call to search for events within 25 miles from the latitude and longitude values we received in the step above. We call the function ShowPosition to render that.
Passing Location To The Discovery API
function showPosition(position) {
var x = document.getElementById("location");
x.innerHTML = "Latitude: " + position.coords.latitude +
"<br>Longitude: " + position.coords.longitude;
var latlon = position.coords.latitude + "," + position.coords.longitude;
$.ajax({
type:"GET",
url:"https://app.ticketmaster.com/discovery/v2/events.json?apikey=pLOeuGq2JL05uEGrZG7DuGWu6sh2OnMz&latlong="+latlon,
async:true,
dataType: "json",
success: function(json) {
console.log(json);
var e = document.getElementById("events");
e.innerHTML = json.page.totalElements + " events found.";
showEvents(json);
initMap(position, json);
},
error: function(xhr, status, err) {
console.log(err);
}
});
}Process the API response
In a case of a successful request to Discovery API, we call function showEvents that processes the response and displays the event list.
Other function initMap initializes Google map and shows markers for events.
Process The API Response
function showEvents(json) {
for(var i=0; i<json.page.size; i++) {
$("#events").append("<p>"+json._embedded.events[i].name+"</p>");
}
}
function initMap(position, json) {
var mapDiv = document.getElementById('map');
var map = new google.maps.Map(mapDiv, {
center: {lat: position.coords.latitude, lng: position.coords.longitude},
zoom: 10
});
for(var i=0; i<json.page.size; i++) {
addMarker(map, json._embedded.events[i]);
}
}
function addMarker(map, event) {
var marker = new google.maps.Marker({
position: new google.maps.LatLng(event._embedded.venues[0].location.latitude, event._embedded.venues[0].location.longitude),
map: map
});
marker.setIcon('http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/ms/icons/red-dot.png');
console.log(marker);
}During the map initialization, we use the addMarker function to add event markers to the map. More details about markers.
You can try this entire tutorial code here.

